Declare @SearchString varchar(50) ='kishor.b'--<--Define your search string here Declare @ResultsFound TABLE(ColumnName nvarchar(370), ColumnValue nvarchar(3630)) SET NOCOUNT ON DECLARE @TableName nvarchar(256), @ColumnName nvarchar(128), @SearchStr2 nvarchar(110) SET @TableName = '' SET @SearchStr2 = QUOTENAME('%' + @SearchString + '%','''') WHILE @TableName IS NOT NULL BEGIN SET @ColumnName = '' SET @TableName = ( SELECT MIN(QUOTENAME(TABLE_SCHEMA) + '.' + QUOTENAME(TABLE_NAME)) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE' AND QUOTENAME(TABLE_SCHEMA) + '.' + QUOTENAME(TABLE_NAME) > @TableName AND OBJECTPROPERTY( OBJECT_ID( QUOTENAME(TABLE_SCHEMA) + '.' + QUOTENAME(TABLE_NAME) ), 'IsMSShipped' ) = 0 ) WHILE (@TableName IS NOT NULL) AND (@ColumnName IS NOT NULL) BEGIN SET @ColumnName = ( SELECT MIN(QUOTENAME(COLUMN_NAME)) FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS WHERE TABLE_SCHEMA = PARSENAME(@TableName, 2) AND TABLE_NAME = PARSENAME(@TableName, 1) AND DATA_TYPE IN ('char', 'varchar', 'nchar', 'nvarchar') AND QUOTENAME(COLUMN_NAME) > @ColumnName ) IF @ColumnName IS NOT NULL BEGIN INSERT INTO @ResultsFound EXEC ( 'SELECT ''' + @TableName + '.' + @ColumnName + ''', LEFT(' + @ColumnName + ', 3630) FROM ' + @TableName + ' (NOLOCK) ' + ' WHERE ' + @ColumnName + ' LIKE ' + @SearchStr2 ) END END END SELECT ColumnName, ColumnValue FROM @ResultsFound
Because sharing knowledge is good. (MSBI, SQL SERVER, Python, Pyspark, Azure Data Factory, Databricks, Machine Learning & Cloud Services)
Find a value in all columns of all tables
Find List of Year, Month,Days On The Basis Of Month Between Two Dates
Declare @StartDate date= '03/01/2015' Declare @EndDate date= '06/05/2015' select year(dt) [Year], month(dt) [Month], count(*) Days from ( select top (datediff(d, @StartDate, @EndDate)) dateadd(d, row_number() over (order by (select null)), @StartDate) dt from sys.columns ) q group by year(dt), month(dt) order by [Year], [Month]
Drop And Recreate all indexes on all tables of a database :
How to use :
First execute both scripts (on SSMS) on your database and save the result. It will generate drop index and create index for all tables on database.
After doing this, please execute drop indexes result and then execute create index result.
Please verify the result.
--First Script----------
---------Drop indexes start
DECLARE @SchemaName VARCHAR(256) DECLARE @TableName VARCHAR(256) DECLARE @IndexName VARCHAR(256) DECLARE @TSQLDropIndex VARCHAR(MAX) DECLARE CursorIndexes CURSOR FOR SELECT schema_name(t.schema_id) , t.NAME , i.NAME FROM sys.indexes i INNER JOIN sys.tables t ON t.object_id = i.object_id WHERE i.type > 0 AND t.is_ms_shipped = 0 AND t.NAME <> 'sysdiagrams' AND ( is_primary_key = 0 AND is_unique_constraint = 0 ) OPEN CursorIndexes FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndexes INTO @SchemaName , @TableName , @IndexName WHILE @@fetch_status = 0 BEGIN SET @TSQLDropIndex = 'DROP INDEX ' + QUOTENAME(@SchemaName) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@TableName) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@IndexName) PRINT @TSQLDropIndex FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndexes INTO @SchemaName , @TableName , @IndexName END CLOSE CursorIndexes DEALLOCATE CursorIndexes --------------------Drop indexes end--------------
PRINT ' '
PRINT '-------- DROP AND CREATE INDEXES BY VIMAL------------------'
PRINT ' '
GO
--Second Script----------
--------------------Create indexes start----------- DECLARE @SchemaName VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @TableName VARCHAR(256) DECLARE @IndexName VARCHAR(256) DECLARE @ColumnName VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @is_unique VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @IndexTypeDesc VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @FileGroupName VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @is_disabled VARCHAR(100) DECLARE @IndexOptions VARCHAR(max) DECLARE @IndexColumnId INT DECLARE @IsDescendingKey INT DECLARE @IsIncludedColumn INT DECLARE @TSQLScripCreationIndex VARCHAR(max) DECLARE @TSQLScripDisableIndex VARCHAR(max) DECLARE CursorIndex CURSOR FOR SELECT schema_name(t.schema_id) [schema_name] , t.NAME , ix.NAME , CASE WHEN ix.is_unique = 1 THEN 'UNIQUE ' ELSE '' END , ix.type_desc , CASE WHEN ix.is_padded = 1 THEN 'PAD_INDEX = ON, ' ELSE 'PAD_INDEX = OFF, ' END + CASE WHEN ix.allow_page_locks = 1 THEN 'ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON, ' ELSE 'ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = OFF, ' END + CASE WHEN ix.allow_row_locks = 1 THEN 'ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ' ELSE 'ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = OFF, ' END + CASE WHEN INDEXPROPERTY(t.object_id, ix.NAME, 'IsStatistics') = 1 THEN 'STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = ON, ' ELSE 'STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, ' END + CASE WHEN ix.ignore_dup_key = 1 THEN 'IGNORE_DUP_KEY = ON, ' ELSE 'IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ' END + 'SORT_IN_TEMPDB = OFF, FILLFACTOR =' + CASE WHEN ix.fill_factor = 0 THEN '100' ELSE CAST(ix.fill_factor AS VARCHAR(3)) END AS IndexOptions , ix.is_disabled , FILEGROUP_NAME(ix.data_space_id) FileGroupName FROM sys.tables t INNER JOIN sys.indexes ix ON t.object_id = ix.object_id WHERE ix.type > 0 AND ix.is_primary_key = 0 AND ix.is_unique_constraint = 0 --and schema_name(tb.schema_id)= @SchemaName and tb.name=@TableName AND t.is_ms_shipped = 0 AND t.NAME <> 'sysdiagrams' ORDER BY schema_name(t.schema_id) , t.NAME , ix.NAME OPEN CursorIndex FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndex INTO @SchemaName , @TableName , @IndexName , @is_unique , @IndexTypeDesc , @IndexOptions , @is_disabled , @FileGroupName WHILE (@@fetch_status = 0) BEGIN DECLARE @IndexColumns VARCHAR(max) DECLARE @IncludedColumns VARCHAR(max) SET @IndexColumns = '' SET @IncludedColumns = '' DECLARE CursorIndexColumn CURSOR FOR SELECT col.NAME , ixc.is_descending_key , ixc.is_included_column FROM sys.tables tb INNER JOIN sys.indexes ix ON tb.object_id = ix.object_id INNER JOIN sys.index_columns ixc ON ix.object_id = ixc.object_id AND ix.index_id = ixc.index_id INNER JOIN sys.columns col ON ixc.object_id = col.object_id AND ixc.column_id = col.column_id WHERE ix.type > 0 AND ( ix.is_primary_key = 0 OR ix.is_unique_constraint = 0 ) AND schema_name(tb.schema_id) = @SchemaName AND tb.NAME = @TableName AND ix.NAME = @IndexName ORDER BY ixc.index_column_id OPEN CursorIndexColumn FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndexColumn INTO @ColumnName , @IsDescendingKey , @IsIncludedColumn WHILE (@@fetch_status = 0) BEGIN IF @IsIncludedColumn = 0 SET @IndexColumns = @IndexColumns + QUOTENAME(@ColumnName) + CASE WHEN @IsDescendingKey = 1 THEN ' DESC, ' ELSE ' ASC, ' END ELSE SET @IncludedColumns = @IncludedColumns + QUOTENAME(@ColumnName) + ', ' FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndexColumn INTO @ColumnName , @IsDescendingKey , @IsIncludedColumn END CLOSE CursorIndexColumn DEALLOCATE CursorIndexColumn SET @IndexColumns = substring(@IndexColumns, 1, len(@IndexColumns) - 1) SET @IncludedColumns = CASE WHEN len(@IncludedColumns) > 0 THEN substring(@IncludedColumns, 1, len(@IncludedColumns) - 1) ELSE '' END --print @IndexColumns --print @IncludedColumns SET @TSQLScripCreationIndex = '' SET @TSQLScripDisableIndex = '' SET @TSQLScripCreationIndex = 'CREATE ' + @is_unique + @IndexTypeDesc + ' INDEX ' + QUOTENAME(@IndexName) + ' ON ' + QUOTENAME(@SchemaName) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@TableName) + '(' + @IndexColumns + ') ' + CASE WHEN len(@IncludedColumns) > 0 THEN CHAR(13) + 'INCLUDE (' + @IncludedColumns + ')' ELSE '' END + CHAR(13) + 'WITH (' + @IndexOptions + ') ON ' + QUOTENAME(@FileGroupName) + ';' IF @is_disabled = 1 SET @TSQLScripDisableIndex = CHAR(13) + 'ALTER INDEX ' + QUOTENAME(@IndexName) + ' ON ' + QUOTENAME(@SchemaName) + '.' + QUOTENAME(@TableName) + ' DISABLE;' + CHAR(13) PRINT @TSQLScripCreationIndex PRINT @TSQLScripDisableIndex FETCH NEXT FROM CursorIndex INTO @SchemaName , @TableName , @IndexName , @is_unique , @IndexTypeDesc , @IndexOptions , @is_disabled , @FileGroupName END CLOSE CursorIndex DEALLOCATE CursorIndex ----------------------Create indexes end--------
SQL Features & Versions
Sql Server 2000 :
- Version 8
- Query analyser & enterprise manager are seperate
- We can create 65535 databases only
- Datetime datatype used for both date & time
Sql Server 2005 :
- Version 9
- Query analyser & enterprise manager are combined as SSMS
- XML datatype is introduced
- We can create max (2^20-1) databases
- Ranking functions (Row_Number, Rank, Dense_Rank, Ntile for paging)
- varchar(max) datatype
- Exception Handling (Try catch block)
- Database mirroring
- CTE (Common table expression)
- Pivot, Unpivot
- Cube, Rollup, Grouping set
- Synonyms
- Bulk copy insert
- DDL triggers
- Table fragmentation
- Full text search
- Can compress the table & indexes (In sql 2005 SP2)
- SSIS introduced
- Table datatype introduced
Sql Server 2008 :
- Version 10
- XML datatype used
- Initialize variables (Declare & initialize variable in single statement)
- Compound assignment operators (+=, -=, *=, /=, %=)
- Enhanced convert function (Conversion between binary & hexadecimal)
- Merge statement
- Filtered Index
- Change data capture
- Can encrypt entire db in 2008 introduced
- PBM (Policy based management) introduced
- CMS (Centralized management server) introduced
- Table datatype available
- Date, time,geospatial,timestamp introduced for different date time format
Sql Server 2008 R2 :
- Version 10.50
- PowerPivot for sharepoint, excel
- Multi-server administration & data-tier application
- Master data services introduced
- Extended protection to connect database engine
Sql Server 2012 :
- Version 11
- AlwaysOn Availability Groups HADR (High Availability and Disaster Recovery)
- Column store Index introduced
- User-defined server roles
- Sql Server data tool for BI
- Order by clause with Offset/fetch option
- New features to sql try_convert(), format()
- In-memory OLTP introduced
Sql Server 2014 :
- Version 12
- In-memory OLTP extended
- Column store Index extended
- Resource governor for I/O & I/O control
- Incremental statistics
- Most other features are related to Sql Azure
Sql Server 2016 :
- Version CTP3.2
- Integration with Hadoop
- Data masking
- Live execution plan
- Row level security
- Non Clustered Index Key length in SQL Server 2016 CTP 3.0 has been increased from 900 bytes to 1700 bytes
SQL Versions & Builds :
| RTM (no SP) | SP1 | SP2 | SP3 | SP4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
codename vNext | 14.0.1000.169 *new | ||||
| 13.0.1601.5 | 13.0.4001.0 or 13.1.4001.0 | 13.0.5026.0 or 13.2.5026.0 | |||
| 12.0.2000.8 | 12.0.4100.1 or 12.1.4100.1 | 12.0.5000.0 or 12.2.5000.0 | |||
codename Denali | 11.0.2100.60 | 11.0.3000.0 or 11.1.3000.0 | 11.0.5058.0 or 11.2.5058.0 | 11.0.6020.0 or 11.3.6020.0 | 11.0.7001.0 or 11.4.7001.0 |
codename Kilimanjaro | 10.50.1600.1 | 10.50.2500.0 or 10.51.2500.0 | 10.50.4000.0 or 10.52.4000.0 | 10.50.6000.34 or 10.53.6000.34 | |
codename Katmai | 10.0.1600.22 | 10.0.2531.0 or 10.1.2531.0 | 10.0.4000.0 or 10.2.4000.0 | 10.0.5500.0 or 10.3.5500.0 | 10.0.6000.29 or 10.4.6000.29 |
codename Yukon | 9.0.1399.06 | 9.0.2047 | 9.0.3042 | 9.0.4035 | 9.0.5000 |
codename Shiloh | 8.0.194 | 8.0.384 | 8.0.532 | 8.0.760 | 8.0.2039 |
codename Sphinx | 7.0.623 | 7.0.699 | 7.0.842 | 7.0.961 | 7.0.1063 |
All SQLServer service packs are cumulative, meaning that each new service pack contains all the fixes that are included with previous service packs and any new fixes.
Reference :
Recover Deleted data on Sql Server
Hi Today I will tell you how to recover the data in case data is deleted Please follow step by step & execute next step when first step will be finished.Step 1 : Create a new fresh database and a table inside this database
USE master
GO CREATE DATABASE TestDb GO USE TestDb GO CREATE TABLE TestTable ( id INT identity(1, 1) ,NAME VARCHAR(50) ,Value INT ,ValueAt DATETIME DEFAULT(GetDate()) ) GO
Step 2 : Create a Full Backup of this database
BACKUP DATABASE TestDb TO DISK = 'D:\TestDb_Full.bak' WITH init ,format ,stats = 10 GO
Step 3 : Follow below DML On table dbo.TestTable
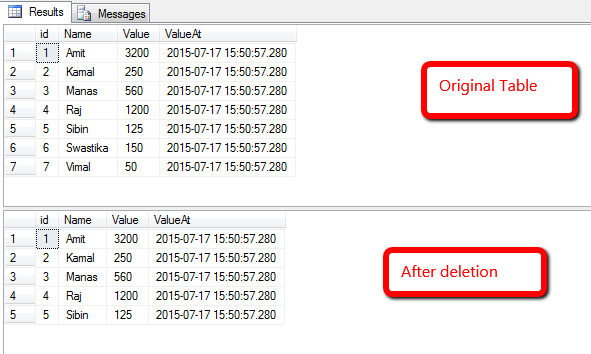
USE TestDb GO INSERT INTO TestTable ( NAME,Value) SELECT 'Vimal' ,50 UNION SELECT 'Kamal' ,250 UNION SELECT 'Raj' ,1200 UNION SELECT 'Swastika',150 UNION SELECT 'Sibin' ,125 UNION SELECT 'Manas' ,560 UNION SELECT 'Amit' ,3200 GO SELECT * FROM TestTable GO DELETE FROM TestTable WHERE id > 5 GO SELECT * FROM TestTable GO
Step 4 : As data has been deleted. Now its time to recover that data.
Note : Here database is new & so as table. It is easy to recover. If you know the time of deleted data or approximate time you can recover data. But you will find it difficult if time range is too long or you forgot the time.
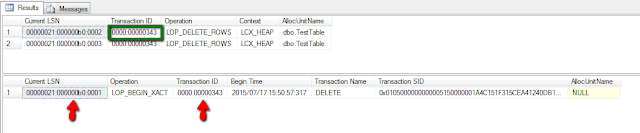
SELECT [Current LSN]
,[Transaction ID]
,[Operation]
,[Context]
,[AllocUnitName]
FROM fn_dblog(NULL, NULL)
WHERE [Operation] = 'LOP_DELETE_ROWS'
AND [AllocUnitName] = 'dbo.TestTable'
SELECT [Current LSN]
,[Operation]
,[Transaction ID]
,[Begin Time]
,[Transaction Name]
,[Transaction SID]
,[AllocUnitName]
FROM fn_dblog(NULL, NULL)
WHERE [Transaction ID] = '0000:00000343'--<<Paste the TransactionID
AND [Operation] = 'LOP_BEGIN_XACT'--Copy CurrentLSN 00000021:000000b0:0001 SELECT CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x00000021', 1)) --Same Value SELECT CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x000000b0', 1)) --Total 10 digit preceeded by 0 SELECT CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x0001', 1)) --Total 5 digit preceeded by 0 -->33000000017600001 SELECT Cast(CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x00000021', 1)) AS VARCHAR(5)) + RIGHT('0000000000' + CAST(CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x000000b0', 1)) AS NVARCHAR), 10) + RIGHT('00000' + CAST(CONVERT(INT, CONVERT(VARBINARY, '0x0001', 1)) AS NVARCHAR), 5) AS 'MarkPoint' GO
Step 5 : Take a log backup now. For this recovery model of database should be Full or Bulk-logged(Right click on Database>>Properties>>Options>>Recovery Model)
BACKUP log TestDb TO DISK = 'D:\TestDb_log.trn' GOStep 6 : Restore Full backup of database
-- Starting first with restoring the FULL BACKUP with NORECOVERY RESTORE filelistonly FROM DISK = 'D:\TestDb_Full.bak'; RESTORE DATABASE [TestDb_New] FROM DISK = 'D:\TestDb_Full.bak' WITH MOVE 'TestDb' TO 'C:\TestDb.mdf' ,MOVE 'TestDb_log' TO 'C:\TestDb_log.ldf' ,REPLACE ,NORECOVERY; GOStep 7 : Restore log backup of database like below
RESTORE LOG TestDb_New FROM DISK = 'D:\TestDb_log.trn' WITH STOPBEFOREMARK = 'lsn:33000000017600001' GO
Step 8 : Check the table data
USE TestDb_New GO SELECT * FROM dbo.TestTable
--Export the deleted rows from this table to original table
Step 9 : Drop tables
USE master GO DROP DATABASE TestDb DROP DATABASE TestDb_New
-->The End<--
Note : Step 4 time range SELECT [Current LSN] ,[Operation] ,[Transaction ID] ,[Begin Time] ,[Transaction Name] ,[Transaction SID] ,[AllocUnitName] FROM fn_dblog(NULL, NULL) WHERE --[Operation] = 'LOP_BEGIN_XACT' --and [Begin Time] BETWEEN '2015/07/17 15:30:00:000' AND '2015/07/17 16:00:00:000'
Store a file & Retrive it in Sql Server
/* Created By : Vimal Lohani on 12-May-2015 */ --Create Table create table #FileSaveTest (Files varbinary(max), name varchar(200))
--Insert file & information
insert into #FileSaveTest (Files, name) select img.*, 'abc.jpg' from openrowset(bulk 'D:\b\abc.jpg', Single_Blob) img --Show table data select * from #FileSaveTest
--Configure advance options
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; go reconfigure; go sp_configure 'Ole Automation Procedures', 1; go reconfigure; go --Retrieve file at a location (Path) declare @FileData varbinary(max); select @FileData = ( select convert(varbinary(max), Files, 1) from #FileSaveTest ); declare @Path nvarchar(200) select @Path = 'D:\a a\'; declare @Filename nvarchar(1024); select @Filename = ( select name from #FileSaveTest ); declare @FullPathToOutputFile nvarchar(2048); select @FullPathToOutputFile = @Path + '\' + @Filename; declare @ObjectToken int exec sp_OACreate 'ADODB.Stream', @ObjectToken output; exec sp_OASetProperty @ObjectToken, 'Type', 1; exec sp_OAMethod @ObjectToken, 'Open'; exec sp_OAMethod @ObjectToken, 'Write', null, @FileData; exec sp_OAMethod @ObjectToken, 'SaveToFile', null, @FullPathToOutputFile, 2; exec sp_OAMethod @ObjectToken, 'Close'; exec sp_OADestroy @ObjectToken;
sp_configure 'Ole Automation Procedures', 0; go reconfigure; go sp_configure 'show advanced options', 0; go reconfigure; go --Drop table drop table #FileSaveTest
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)